Apple introduced its own AI – Apple Intelligence
After months of rumors, Apple has finally unveiled Apple Intelligence, which will offer users more than just generative images. At the end of the keynote presentation at WWDC 2024, after announcing new operating systems, the company moved into the main event and talked about its commitment to using machine learning.
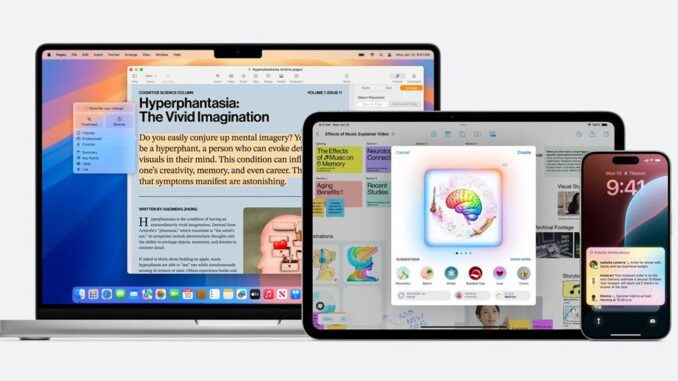
The new service, called Apple Intelligence, uses large language models (LLMs) to perform tasks related to text, images and actions within applications.
To start, the system is able to summarize key notifications, showing users the most important elements in a context-based summary.
Apple introduced its own AI – Apple Intelligence
System-wide text writing tools can write, proofread, and summarize text for users. This is available automatically in built-in and third-party apps.
Apple Intelligence can also create images for many built-in applications. For example, this includes personalized images for communicating with specific contacts in Messages.
These images are created in three styles: sketch, animation and realism.
In addition, the system can perform actions within applications on behalf of the user. For example, she can open Photos and show images of specific groups of people when requested.
Apple also states that Apple Intelligence focuses on the context of a query within user data. For example, it can determine who the user’s family members are and how encounters may overlap or conflict.
Much of this is based on processing data on the device itself to ensure security and privacy. The A17 Pro chip in the iPhone 15 Pro lineup is powerful enough to handle this level of processing.
Private Cloud Compute
Many models run on the device, but sometimes require cloud processing. This may pose a security issue, but Apple’s method is different. Private Cloud Compute enables Apple Intelligence to run in the cloud while maintaining security and privacy. Models run on Apple Silicon servers using Swift security elements.
Processes on the device determine whether the request is sent to cloud servers or can be processed locally.
Apple insists the servers are secure, do not store user data and use cryptographic elements to maintain security.