
Steam revenues and users growing Italian is non-existent
Valve has revealed some data relating to Steam, talking about users and revenues growing strongly in recent years, especially in some territories, with Italian being non-existent.
Steam revenues and users are growing strongly , especially in some territories. In particular in Asia, Central America and South America. Valve’s Kassidy Gerber told it at the Nordic Game 2024, who gave a speech explaining the progress of the strongest digital delivery platform in the world .
The key points of his speech concern the growth of Steam over the last five years. For example, he indicated some of the countries in which the store has grown the most in terms of number of users: China, Serbia and the Philippines have seen a 100% increase in registered users, while Japan, India and Mexico have seen a 150% increase. These are enormous numbers that make it clear why Valve is looking more and more in that direction and why games coming from those territories are multiplying.
Mind-boggling numbers
“Part of our mission is to reach gamers around the world,” Gerber explained. “We invest a lot in making sure we have prices in the correct currencies, accept the best payment methods and connect our servers with our customers.”
Steam revenues and users growing Italian is non-existent
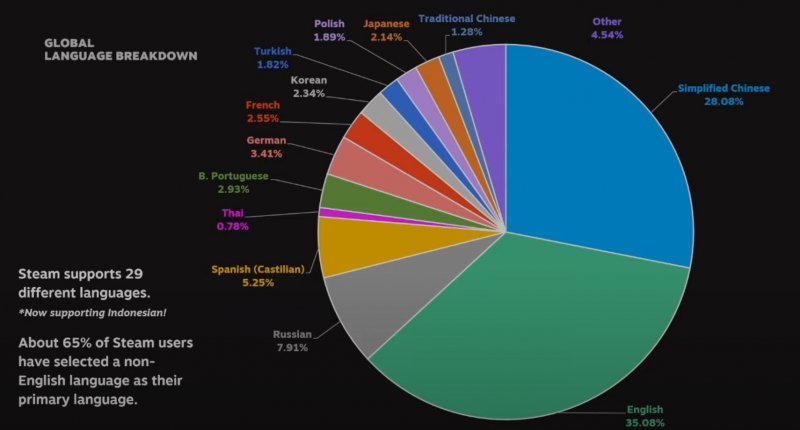
Steam currently supports 29 languages , but Valve wants to grow that number. He also revealed that the most used ones are different from what many believe, with Italian practically not existing . In the lead is English with 35.08%, followed by Simplified Chinese with 28.08%, Russian with 7.91%, Castellano Spanish with 5.25% and German with 3 ,41%. As mentioned, Italian is not among the most widespread languages, i.e. it is in the “Others” item which overall includes 4.54% of users and which includes languages used by less than 0.78% of users. So it should be clearer why many no longer translate their games into Italian.
As for revenues, the platform saw enormous growth during the pandemic period , with the platform normalizing after the end of the pandemic, without however going into deficit. Gerber highlighted how sales are one of the main drivers of growth, which is constant over the years, with sales getting better and better. For example, average revenues from summer sales grew by 23% year over year, those from autumn sales by 17% and those from winter sales by 13%. It should be underlined that the latter two still produce more revenue than the other event. Furthermore, the growth does not only concern major games, but also medium and small productions.